The resistance of polymer materials to external factors is not limitless. The main threats can be systematized as follows:
Adhering to these principles will preserve the original properties of the netting throughout its storage life.
A racking system is recommended for efficient storage and damage minimization.
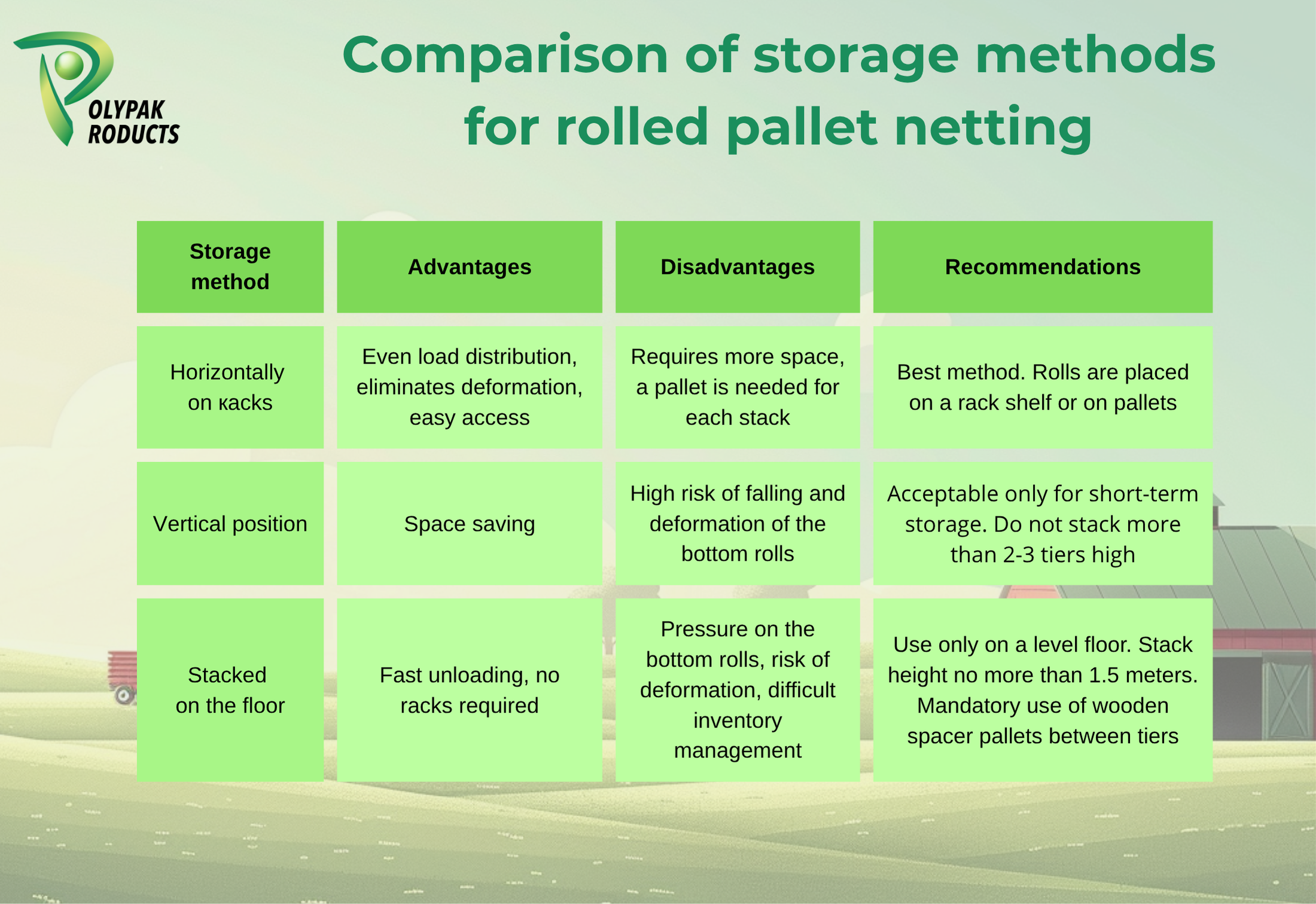
Clear batch labeling and warehouse organization according to the FIFO principle prevent the accumulation of old netting and its natural degradation over time.
Pallet netting is a reliable and economical product, whose potential is fully realized only when the rules of operation are followed, starting from the warehouse. Organizing proper storage conditions is not an additional cost item, but a strategic investment in the continuity of your logistics processes, cargo safety, and overall business efficiency. An approach based on understanding the properties of polymer materials and following these simple recommendations guarantees that every roll of netting will deliver its full performance potential. Please contact us if you have any questions.
2020 All Rights Reserved.
2020 All Rights Reserved.